-
Review
-
Original Paper
 28 February 2026
28 February 2026 -
Original Paper
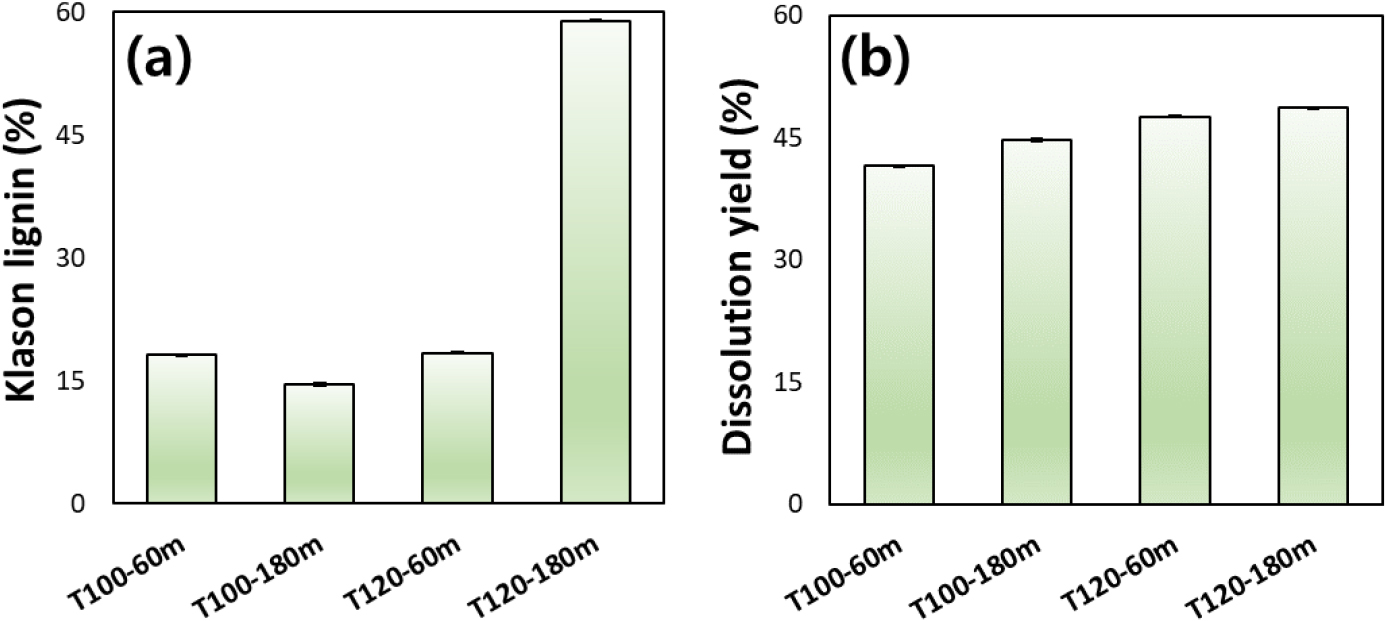
- Effect of Pulping Condition on Bamboo Pulp Properties in Glycol Ether-Based Organosolv Process
- Sa Rang Choi, Jiae Ryu, Jung Myoung Lee
-
Original Paper
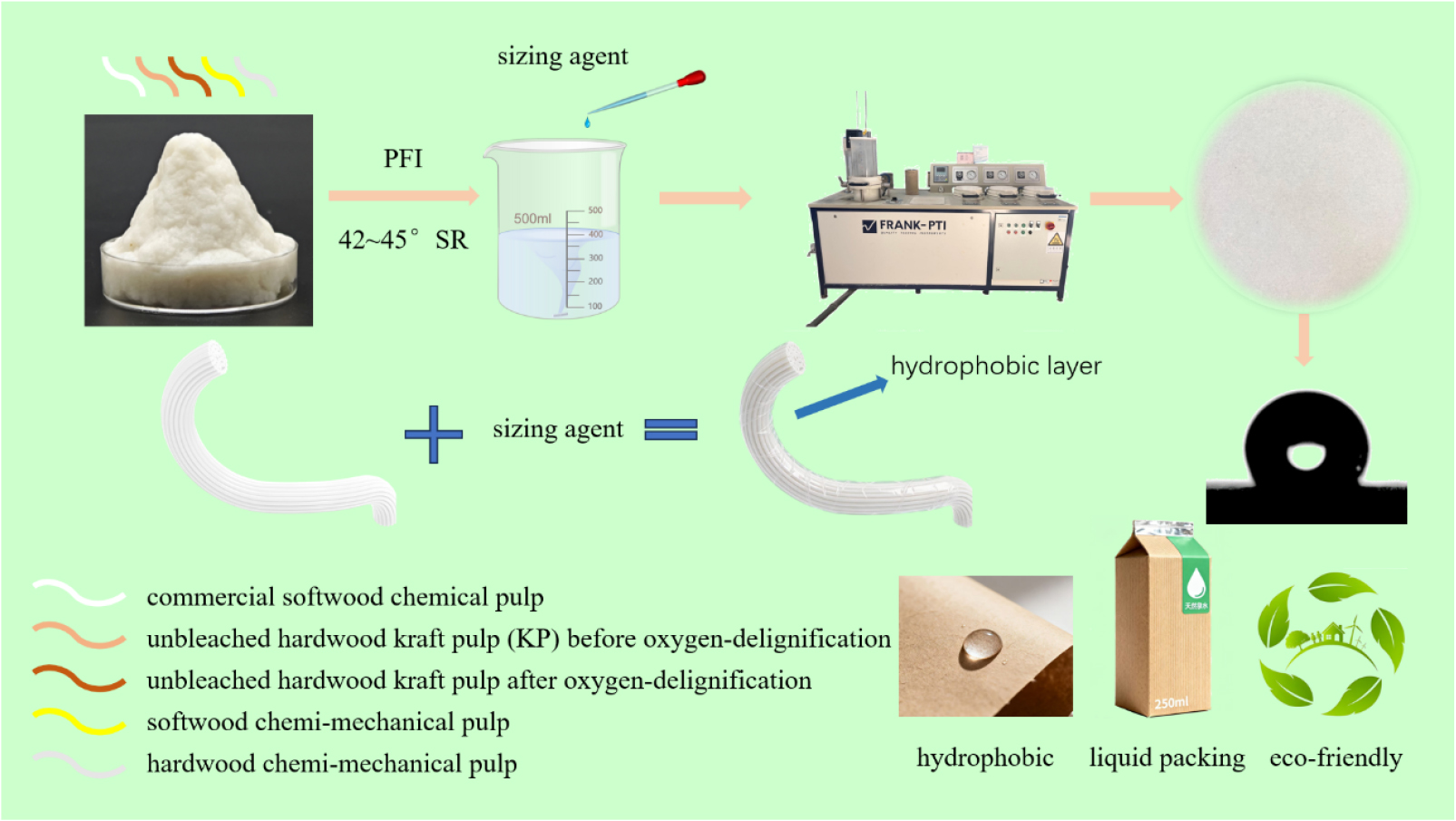
- Influence of Sizing Treatment on the Hydrophobicity and Strength Properties of Cellulose-Based Paper Materials for Liquid Packaging
- Hao Liu, Guihua Yang, Ming He, Shaoguang Wang, Qimeng Jiang, Chenyue Yu, Jiachuan Chen
-
Original Paper
-
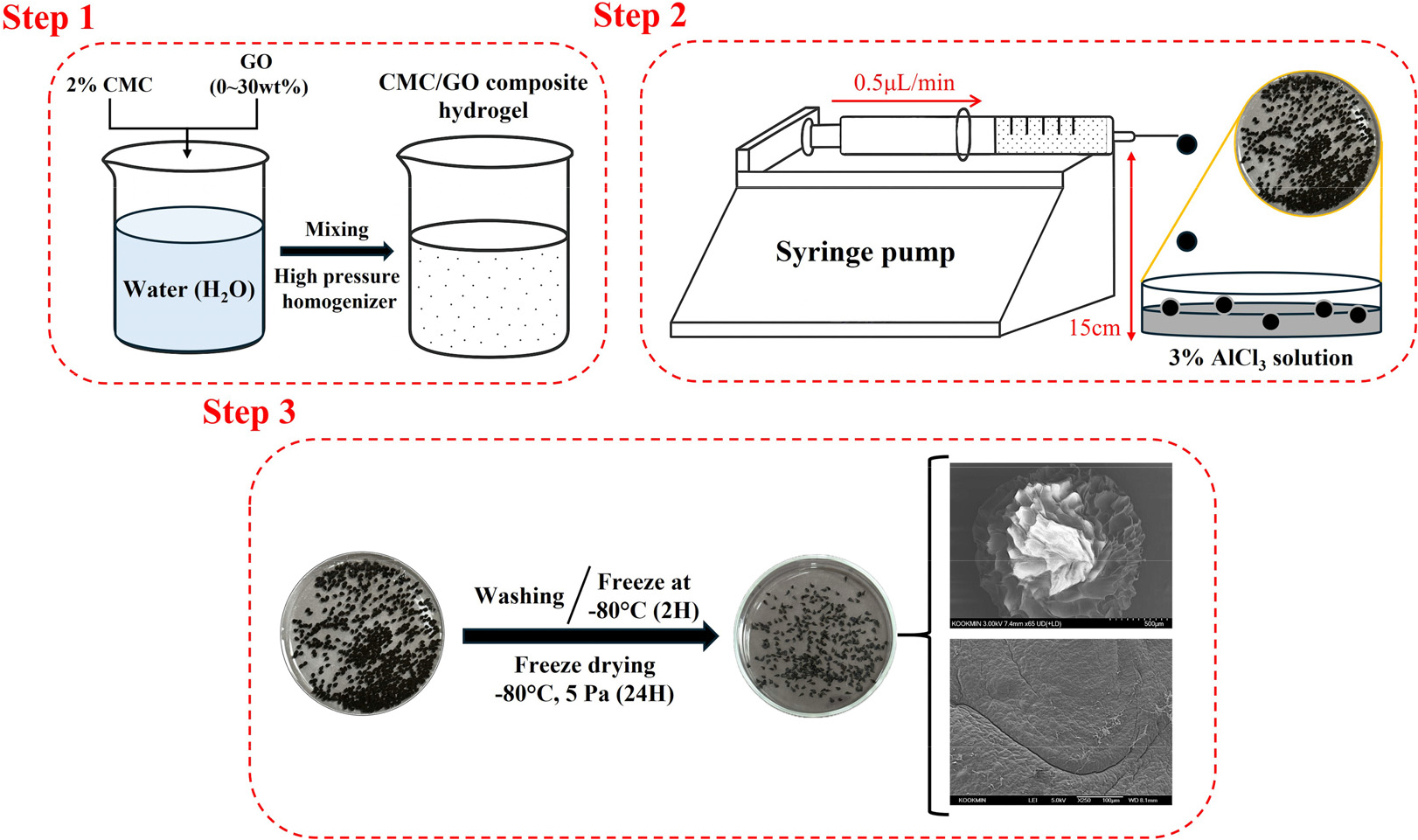
Fabrication of Carboxymethyl Cellulose/Graphene Oxide Composite Beads and Evaluation of Their Adsorption Behavior for Efficient Removal of Methylene Blue from Aqueous Solutions
수용액 내 메틸렌블루 제거를 위한 카르복시메틸셀룰로오스/그래핀옥사이드 복합 비즈 제조 및 흡착 거동 평가
-
Jae-Young Kim, Soon Wan Kweon, Dae-Hyun Jang, Hyoung Jin Kim, Jae Ho Ryu, Tai Ju Lee
김재영, 권순완, 장대현, 김형진, 류재호, 이태주
-
Fabrication of Carboxymethyl Cellulose/Graphene Oxide Composite Beads and Evaluation of Their Adsorption Behavior for Efficient Removal of Methylene Blue from Aqueous Solutions
-
Original Paper
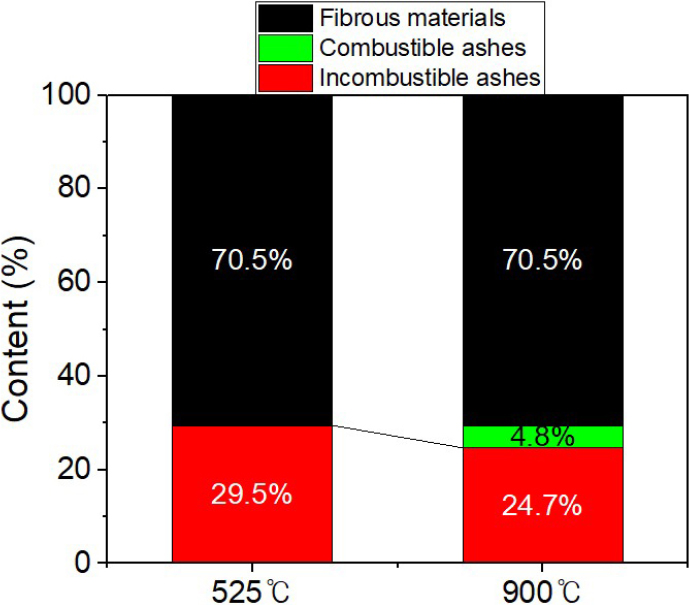
-
Nanofibrillation of White Water Solids and Their Application to Papermaking Process
백수 고형분의 나노피브릴화 및 이의 제지공정 적용
-
Seung-wook Park, Kunhee Lee, Hakmyoung Lee, Hye Jung Youn
박승욱, 이건희, 이학명, 윤혜정
-
Nanofibrillation of White Water Solids and Their Application to Papermaking Process
-
Original Paper
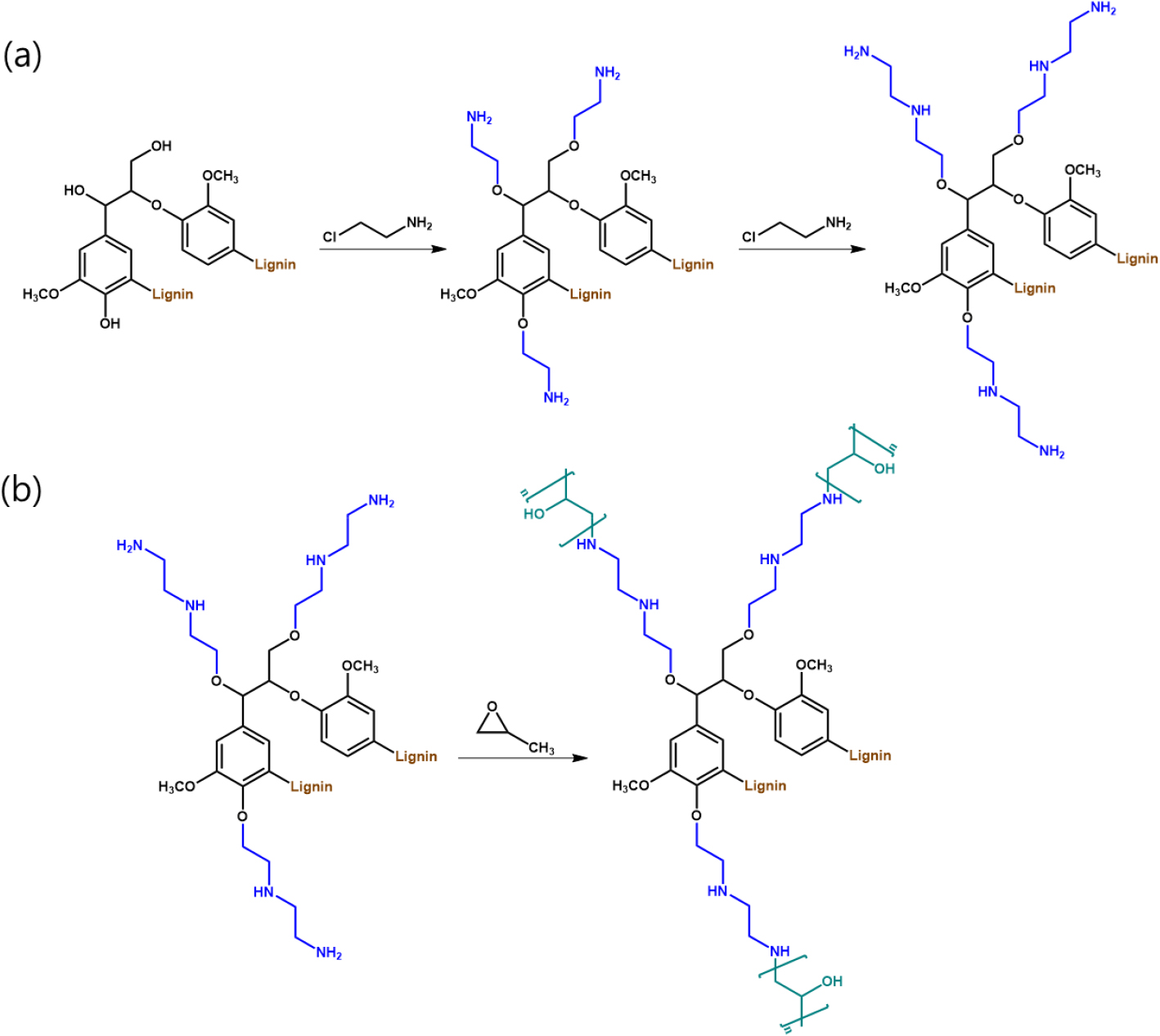
-
Dual-Functional Lignin via Amination and Oxypropylation for High-Strength Hydrogels with Enhanced Network Integrity
아민화 및 옥시프로필화를 통한 이중 기능화 리그닌 기반 고강도 하이드로겔의 네트워크 안정성 향상
-
Min Soo Kim, Ji Won Heo, Yong Sik Kim
김민수, 허지원, 김용식
-
Dual-Functional Lignin via Amination and Oxypropylation for High-Strength Hydrogels with Enhanced Network Integrity
-
Original Paper
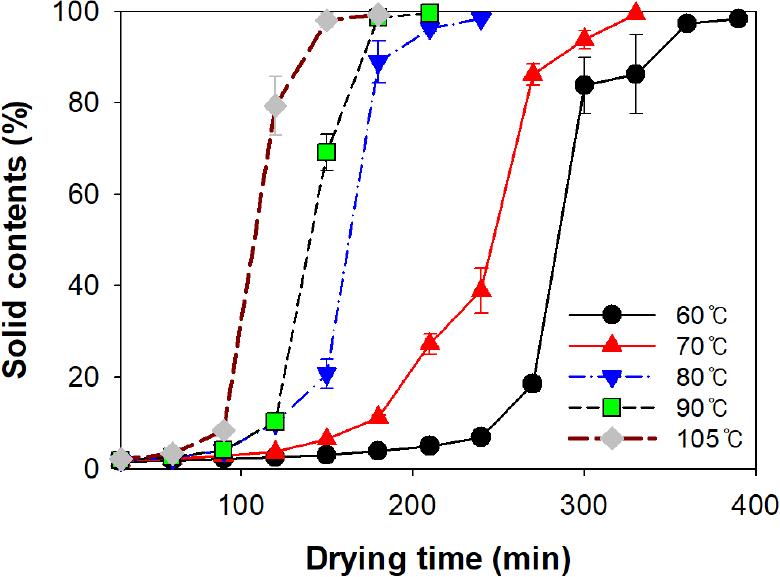
-
Effect of Drying Temperature on Network Structural and Absorption-Retention Properties of CMC/Starch-Based Superabsorbent Polymers
건조 온도가 CMC/전분-기반 고흡수성 소재의 네트워크 구조 및 흡수·보수 특성에 미치는 영향
-
Ha-Neul Kim, Byoung-Uk Ch
김하늘, 조병욱
-
Effect of Drying Temperature on Network Structural and Absorption-Retention Properties of CMC/Starch-Based Superabsorbent Polymers
-
Original Paper
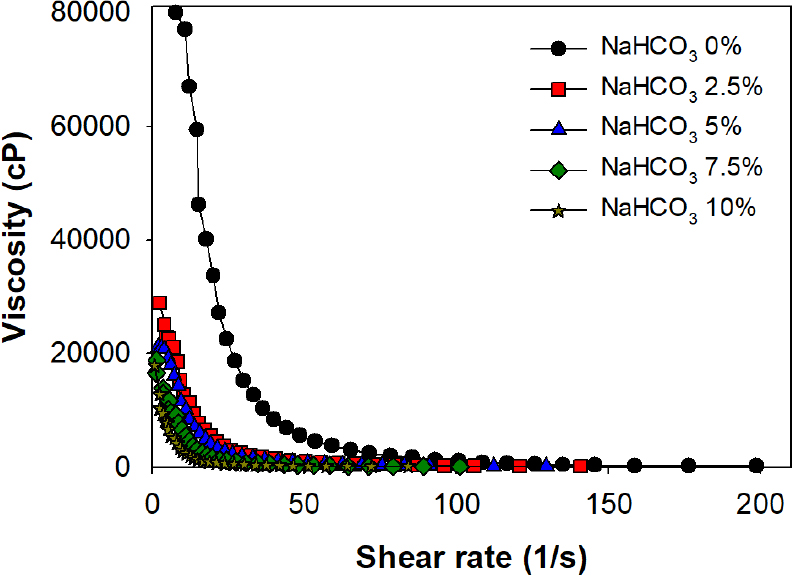
-
Enhancement of Saline Absorbency in CMC/Starch-Based Superabsorbent Polymers by Incorporation of Sodium Bicarbonate
중탄산나트륨 첨가에 따른 CMC/전분 기반 고흡수성 고분자의 염수 흡수 특성 향상
-
Chan Hee Shin, Young Lae Kim, Byoung-Uk Cho
신찬희, 김영래, 조병욱
-
Enhancement of Saline Absorbency in CMC/Starch-Based Superabsorbent Polymers by Incorporation of Sodium Bicarbonate



 Journal of Korea TAPPI
Journal of Korea TAPPI







